

There is no cure for auditory neuropathy. Treatment options for auditory neuropathy other tests – to rule out other conditions that may present similar symptoms, such as multiple sclerosis.Generally speaking, a person with auditory neuropathy performs poorly when the test is given with background noise other hearing tests – such as speech recognition.
Typically, a person with auditory neuropathy has some properly functioning hair cells If so, the microphone will pick up the faint sounds made by the hairs as they respond to noise. otoacoustic emissions (OAE) – a tiny microphone is placed inside the ear canal to check whether the cochlear hair cells are working.Typically, a person with auditory neuropathy has little or no response
#Auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder recommendaions series

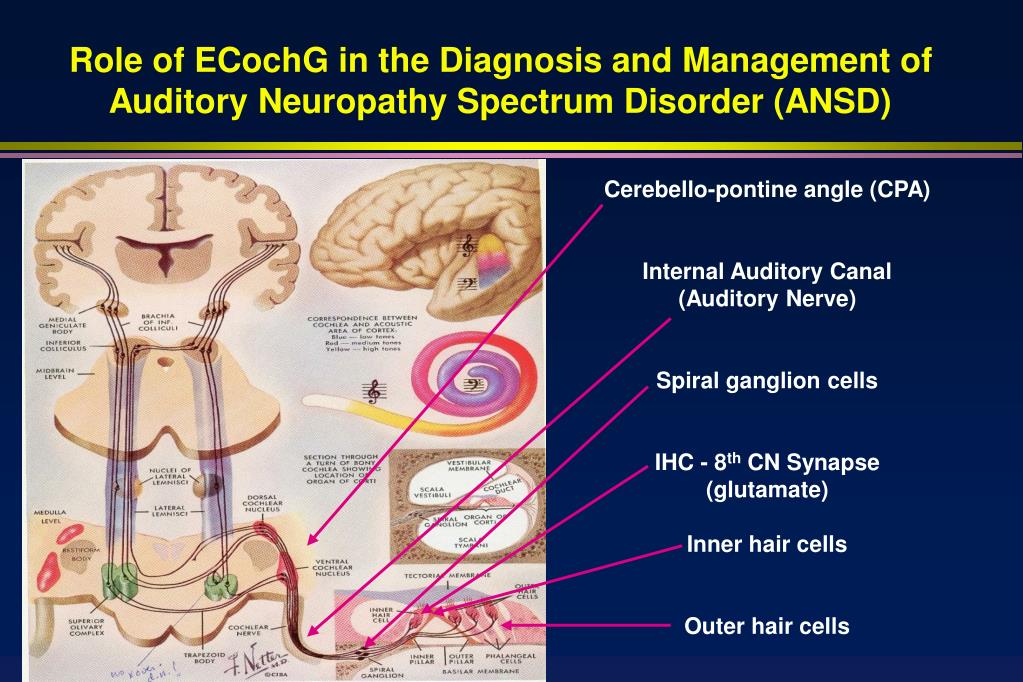
middle ear – separated from the outer ear by the eardrum.Sounds are funnelled into the middle ear by the outer ear The different structures involved in hearing include: Many of the symptoms of auditory neuropathy can also be caused by more common types of hearing loss. worsened speech perception in noisy environments.normal hearing but with poor speech perception.difficulty understanding spoken words (speech perception).The symptoms of auditory neuropathy vary from one person to the next, and can fluctuate. For example, the hearing of a person diagnosed with auditory neuropathy may improve, deteriorate or remain unchanged, and there is no way to predict the outcome. Symptoms of auditory neuropathy can sometimes vary for example, a person may experience both improvements and deteriorations in their hearing. Hearing and understanding speech may be improved by the use of hearing aids or cochlear implants. In some cases, the affected person can hear, but has difficulty understanding spoken words, particularly in noisy environments. Auditory neuropathy is sometimes referred to as a form of neural or nerve deafness. Both ears are usually affected, and the hearing loss ranges from mild to severe. It is caused by disruption of the nerve impulses travelling from the inner ear to the brain, although what causes this is unknown, and there is no cure. Auditory neuropathy is a rare type of hearing loss.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
